
Cannabis has been used for centuries for a variety of purposes, including medicinal and recreational use. Recently, medicinal cannabis has gained popularity due to its potential therapeutic benefits. This guide covers all aspects of medicinal cannabis. Benefits, history, strains, scientific research, uses and legalization are discussed. Learn everything you need to know about medical cannabis!
As more and more countries legalise medicinal cannabis, it is important to understand the science behind this powerful plant. In this comprehensive guide, you'll learn everything you need to know about medicinal cannabis, from the history of cannabis as a medicine to the different strains and their medicinal properties.
We cover the latest medical research and practical information on the use of cannabis for various medical conditions. Whether you are a healthcare professional or a patient seeking alternative treatments, this guide will give you the knowledge you need to safely navigate the world of medical cannabis.
Cannabis, commonly known as marijuana, is a plant containing over 140 active compounds called cannabinoids. The most well-known cannabinoids are tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). THC is responsible for the psychoactive effects or "high" associated with cannabis, whereas CBD does not produce a high and may offer potential medicinal benefits. Cannabis has been used for both medicinal and recreational purposes for thousands of years, with historical use dating back to ancient China and India.
Cannabinoids are the active compounds in cannabis that contribute to its potential therapeutic effects. With over 140 known cannabinoids, THC and CBD are the most prominent. THC is the psychoactive compound that induces the high associated with cannabis, while CBD is non-intoxicating and may offer medical benefits.
Cannabinoids interact with the body's endocannabinoid system (ECS), which regulates functions such as pain, mood, and appetite. By binding to specific receptors in the ECS, cannabinoids can influence these physiological processes (2).
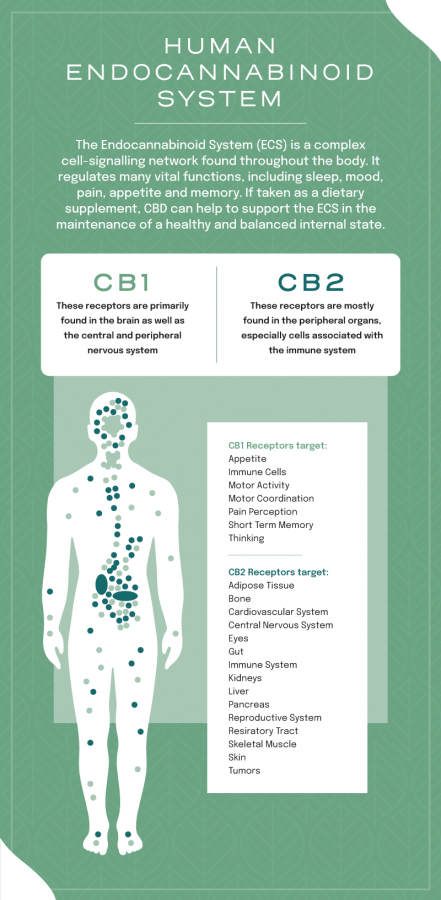
The ECS is a complex network of receptors and neurotransmitters involved in the regulation of various physiological processes, including pain perception, mood, appetite and immune function. CBD interacts with the ECS in several ways, including inhibiting the breakdown of endocannabinoids and binding to specific receptors in the ECS.

Cannabidiol (CBD) is a cannabinoid found in cannabis that has received considerable attention in recent years for its potential therapeutic benefits. Unlike THC, CBD does not produce a "high" and is often used for its medicinal properties. CBD has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects, counteract anxiety and relieve pain (3).
One of the most important ways CBD works in the body is through its interaction with the endocannabinoid system (ECS).
CBD is available in various forms including oils, tinctures, capsules and topical applications. It is also found in some cannabis strains, although the CBD content of these strains can vary widely. CBD products are legal in many parts of the world, although this legality can vary depending on local and national laws. It is important that you become familiar with one
Consult your doctor before using CBD or any other cannabis product for medical purposes.
THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, is the main psychoactive compound in cannabis. It creates the 'high' or altered state of consciousness that recreational users seek. However, THC also has potential medical uses. It has been shown to have pain relief and anti-inflammatory properties and may also help with nausea and vomiting (4).

Medical cannabis is cannabis used for medicinal purposes. It is prescribed by doctors to treat a variety of ailments, including chronic pain, multiple sclerosis, epilepsy, and nausea caused by cancer treatment. Medical cannabis is available in various forms, including vaping flowers, edibles, oils and tinctures.
Yes, medical cannabis is the same as recreational cannabis in that it is used for medicinal purposes under the guidance of a doctor. There are also high-CBD options that can be prescribed as balanced strains (for example, the ratio of THC to CBD is 1:1). However, the most commonly prescribed flower is the high THC flower.
Yes, there is scientific evidence to support the use of cannabis for medicinal purposes. Over the years, several studies have been conducted to investigate the medicinal benefits of cannabis and the results have been promising.
Cannabis contains several active compounds, the most well-known being tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). Both THC and CBD have been shown to be therapeutically effective, with THC being the main component responsible for the plant's psychoactive properties and pain relief.
Below are some of the medicinal uses of cannabis that are supported by scientific research:
1. Pain relief: Cannabis has been shown to be effective in the treatment of chronic pain, particularly multiple sclerosis, neuropathic pain and cancer-related pain (5).
2. Anti-inflammatory effects: CBD in particular has been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties, making it useful in the treatment of diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis (6).
3. Anxiety and depression: Cannabis has been found to have anti-anxiety and anti-depressant effects, making it useful in the treatment of anxiety and depression (7).
4. Epilepsy: Cannabis has been shown to be effective in reducing seizures in people with certain types of epilepsy, such as Dravet syndrome and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome (8).
5. Nausea and vomiting: Cannabis has been shown to be useful in the treatment of nausea and vomiting caused by chemotherapy and other treatments (9).

Like any medicine, medical cannabis can have side effects. However, the severity of these side effects varies depending on the person and the amount of cannabis consumed. Below are some of the most common side effects of consuming medical cannabis:
The two main types of medical cannabis are Indica and Sativa. Indica strains have a relaxing effect on the consumer, while sativa is more stimulating. Hybrid strains combine indica and sativa for a balanced effect that can be either stimulating or calming, depending on the specific blend of the plant. It's important to know that the effects of each strain vary from person to person and depend on factors such as method of consumption, dosage, potency, body chemistry, and tolerance.
Another crucial aspect of medicinal cannabis is understanding the difference between CBD (cannabidiol) and THC (tetrahydrocannabinol). While THC is responsible for the psychoactive effects commonly associated with marijuana use, CBD has medicinal properties without causing a high.
Cannabis indica and cannabis sativa are the two main types of cannabis.
wirken entspannender und haben eine beruhigende Wirkung, die Angstzustände und Schlaflosigkeit lindern kann.
On the other hand Sativa varieties tend to be more stimulating and energizing, making them suitable for daily consumption.
Both indica and sativa strains have unique chemical profiles that have different effects on the body.
Medical cannabis is becoming increasingly popular as a treatment option for a variety of conditions such as chronic pain, anxiety disorders, epilepsy and cancer-related symptoms. Indica strains are often used to relieve pain and treat insomnia, while sativa strains boost creativity or energy levels if you suffer from depression or fatigue.
These combine the properties of indica and sativa plants to create unique effects tailored to individual needs. The benefits of hybrid cannabis include increased potency without the excessive drowsiness or paranoia that occurs with pure THC strains; additional medicinal benefits such as anti-inflammatory properties that reduce joint swelling, causing less pain when moving about in daily life; Enhanced flavor through hybridisation techniques that combine multiple terpenes, resulting in a distinct aroma reminiscent of sweet fruits like mango, mixed with spicy pepper notes for an overall exotic experience!
Cannabis Sativa and Cannabis Indica are two different species within the genus Cannabis. Although they have similarities, they also have significant differences. Cannabis sativa tends to be larger, has narrow leaves and tends to grow in warmer areas. It is known for its uplifting and energizing effects, making it popular among those looking to increase their concentration and creativity.
Cannabis Indica, on the other hand, is shorter and bushier with broader leaves and thrives in cooler climates. Indica strains are often associated with relaxation, calming and a sense of peace, making them a popular means of relaxation and stress relief.
Both sativa and indica strains contain different cannabinoids, including THC and CBD, but their ratios and concentrations can vary, resulting in different effects. Understanding the differences between the two can help individuals choose cannabis strains that suit their desired effects and preferences.
| Feature | Cannabis Sativa | Cannabis Indica |
| Species | Sativa | Indica |
| Appearance | Tall, narrow leaves | Short, bushy, broad leaves |
| Growth Environment | Warmer climates | Cooler climates |
| Effects | Uplifting, energizing | Relaxing, calming |
| Common Uses | Increased concentration, creativity | Stress relief, relaxation |
| Leaf Shape | Narrow leaves | Broad leaves |
| Height | Larger, taller plant | Shorter, bushier plant |
| Cannabinoid Content | Varies; generally higher THC, lower CBD | Varies; often balanced or higher CBD |
Both cannabidiol (CBD) and tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) are natural compounds that come from the cannabis plant. However, they interact with our bodies differently and have different effects.
How CBD and THC interact with the body's endocannabinoid system:
Both CBD and THC bind to cannabinoid receptors in our brains and bodies. However, while THC binds strongly to these receptors and produces a psychoactive effect called a 'high', CBD has a very weak binding affinity.
Medical benefits of CBD compared to THC:
CBD is known for its anti-inflammatory properties and can be used to treat conditions such as chronic pain, anxiety and epileptic seizures, but it also has some medical benefits including relief from nausea/vomiting and muscle cramps/spasms.
The main side-effect of consuming large amounts of THC is a 'high', which can cause temporary impairment in tasks that require coordination or concentration, such as driving or operating heavy machinery, and there are no reports of CBD overdose causing impaired judgement.
It's important to consult your doctor to prescribe the medical cannabis that best suits your needs.
| Feature | CBD | THC |
| Source | Cannabis plant | Cannabis plant |
| Interaction with Endocannabinoid System | Weaker binding affinity to cannabinoid receptors | Strong binding to cannabinoid receptors |
| Psychoactive Effects | Non-intoxicating, no 'high' | Psychoactive, produces a 'high' |
| Medical Benefits | Anti-inflammatory, pain relief, anxiety reduction, seizure control | Pain relief, nausea/vomiting relief, muscle spasms |
| Common Uses | Chronic pain, anxiety, epilepsy, inflammation | Nausea, pain, muscle cramps/spasms, appetite stimulation, reduce symptoms of PTSD, migraines, mental health, and aid in seizure control for epilepsy patients. |
| Side Effects | Mild, usually well-tolerated, no reported overdose | Impaired coordination, concentration, potential temporary impairment |
| Safety Considerations | Consult a doctor before use, generally safe without impairment | High doses can impair judgement; consult a doctor before use |
| Cannabinoid Content | Varies; generally higher THC, lower CBD | Varies; often balanced or higher CBD |
Medicinal cannabis has a long history of medicinal use dating back to antiquity. The plant has been used in various cultures around the world for a variety of purposes such as: B. to relieve pain and improve mood. However, with the advent of modern medicine and pharmaceuticals, cannabis has become illegal and banned in many countries around the world due to its psychoactive properties.
Recently, there has been a trend in many countries around the world to legalise medical cannabis because of its many health benefits. There is now scientific evidence that supports the use of medical marijuana in the treatment of chronic pain, epilepsy and anxiety, among others. This shift in the perception of medical marijuana has led to increased research on how to use it more effectively while minimizing the negative effects associated with it.

Cannabis use dates back thousands of years and there is evidence that ancient civilisations used it for medicinal purposes. Here are some examples:
Cannabis has been used in traditional Chinese medicine since 2700 BC. It has been used to treat a variety of ailments, including pain and insomnia.
Cannabis has been used in Ayurvedic medicine for centuries to treat digestive problems, anxiety and other ailments.
There are records from ancient Greek and Roman times that suggest cannabis was used medicinally for pain relief. These examples show that the medical use of cannabis is not a new phenomenon. People have used it throughout history for its therapeutic properties.
The history of cannabis prohibition laws dates back to the early 20th century, when it was classified as a dangerous drug with no medical value. In recent years, however, there has been a significant global effort to legalise medical cannabis due to its proven therapeutic benefits for various medical conditions.
Medical cannabis has been legalised in several countries because of its therapeutic benefits for various health conditions.
Currently, countries such as the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, Germany and many others have legalised the use of medicinal cannabis under strict regulation and prescription by doctors. In other countries, however, any form of marijuana use remains strictly prohibited, despite growing evidence of the potential health benefits of marijuana.
It is clear that despite progress in the global legalisation of medicinal cannabis, much work still needs to be done to achieve widespread acceptance and awareness of the potential of this natural medicine to improve people's lives.
Medical cannabis has proven to be an effective treatment for pain. By interacting with the body's endocannabinoid system, the compounds in medical cannabis can reduce inflammation and relieve pain. This makes it a promising alternative for people who do not tolerate or respond well to traditional pain medications. In addition, medical cannabis does not pose the same risk of addiction and overdose as many prescription opioids.
Medical cannabis has been shown to be effective in alleviating these symptoms by interacting with CB1 receptors in our brains, reducing feelings of nausea and stimulating appetite.
Medical cannabis research has shown promise for alleviating chronic pain, including migraines, neuropathic pain, cancer-related pain and pain associated with conditions such as multiple sclerosis. Cannabinoids found in cannabis, such as THC and CBD, interact with the body's endocannabinoid system, which plays a role in pain regulation (10).
Medical cannabis has proven to be an effective treatment for neuropathic pain, migraines and arthritis. Neuropathic pain is caused by damage to the nervous system and can be difficult to treat with conventional medications. Medical cannabis contains compounds that interact with the body's endocannabinoid system, which plays a role in regulating pain perception. Migraines are another form of chronic pain that can be treated with medical cannabis.
Arthritis is a common condition that causes inflammation of the joints and can lead to chronic pain. Medical cannabis has been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce swelling and relieve the discomfort associated with arthritis. In addition, some strains of medical cannabis contain high levels of cannabidiol (CBD), a non-psychoactive compound that has been studied for its potential as a painkiller.
Overall, medical cannabis offers promising benefits in the treatment of various types of chronic pain conditions such as neuropathic pain, migraine and arthritis, through its interaction with the body's endocannabinoid system or its anti-inflammatory properties due to its CBD content. However, due to potential side effects or interactions with other medications they may already be taking, it is important that patients considering medical marijuana as a treatment option first consult with their physician before incorporating it into their treatment plan.
Nausea and vomiting associated with chemotherapy, appetite stimulation and pain relief are just some of the unpleasant side effects suffered by cancer patients. Medicinal cannabis has shown promise in alleviating these symptoms, making it a potential complementary treatment for cancer (11).
Medical cannabis offers hope as an alternative or complementary therapy for symptom management during cancer treatment. However, it is important that you first consult with a physician who has experience with medical cannabis before incorporating it into your treatment plan.
Generalised anxiety disorder (GAD), post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and major depressive disorder are three common mental illnesses that can significantly affect a person's quality of life. For people suffering from these disorders, traditional treatments are not always effective or available. However, medical cannabis has shown promising results in treating the symptoms associated with these conditions (13).
Research suggests that CBD helps reduce anxiety in people with GAD and PTSD. THC, another compound found in cannabis, is considered an effective treatment for depression because it increases serotonin levels in the brain.
Although medical cannabis as a whole and its effects on various mental health conditions still require further research, it has great potential as an alternative method for treating anxiety and depressive disorders.

Cannabinoids, particularly THC, have been shown to have antiemetic effects that make medical cannabis an effective treatment option for nausea and vomiting, particularly in patients undergoing chemotherapy or suffering from symptoms associated with other treatments (14).
Medicinal cannabis has shown promise for improving sleep and treating sleep disorders. It can help people with insomnia or conditions that cause sleep disturbances to achieve better quality and length of sleep (15).
The cannabinoids in medical cannabis have anti-inflammatory effects that may be beneficial in the treatment of conditions characterised by chronic inflammation, such as arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease and autoimmune disorders. In addition, medicinal cannabis may modulate the immune system and its responses, potentially promoting immunological diseases (16).
Medical cannabis has gained attention as a potential treatment option for fibromyalgia sufferers. Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain disorder characterised by widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue and sleep disturbances. The cannabinoids in cannabis, such as THC and CBD, have been shown to have analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties that may alleviate some of the symptoms associated with fibromyalgia.
However, further research is needed to fully understand the efficacy, safety and long-term effects of medical cannabis in fibromyalgia. It is important that individuals considering medical cannabis treatment consult with their healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate approach for their specific condition (17).
Medical cannabis has been explored as a potential therapeutic option for people with autism spectrum disorders (ASD). Although research in this area is still limited, some studies suggest that some components of cannabis, particularly CBD (cannabidiol), may have positive effects on symptoms associated with autism. Individuals and families considering treatment for autism with medical cannabis should consult with professionals who are knowledgeable in this area to make an informed decision (18).
Medicinal cannabis is becoming an increasingly popular treatment for a variety of ailments due to its ability to act on the endocannabinoid system (ECS) in the body. The ECS regulates several biological processes, including sleep, appetite and pain perception (26). The cannabinoids in medical cannabis can bind to receptors within the ECS, helping to regulate these processes and alleviate symptoms.
When consumed, cannabinoids such as THC and CBD can affect different parts of the brain and body depending on the concentration and route of ingestion. For example, when cannabis is smoked or vaporised, the onset of effects is faster and lasts for a shorter period of time than when consumed as edibles or tinctures, and more and more medical research is being conducted on the potential therapeutic effects of medicinal cannabis.
The endocannabinoid system is a complex network of receptors, enzymes and signaling molecules that play a key role in maintaining balance and homeostasis in the body. It consists of two main receptors, CB1 and CB2, which are found throughout the central nervous system, peripheral tissues and organs.
The functions of the endocannabinoid system include the regulation of appetite, mood, sleep, immune function, pain perception, memory formation, and processing of equipment. Endocannabinoids, such as anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol, bind to these receptors and produce a variety of effects in the body, including anti-inflammatory effects. The therapeutic potential of medicinal cannabis lies in its ability to interact effectively with this system.
Endocannabinoids affect various physiological functions in our body by binding or activating specific cannabinoid receptor proteins on the surface of cells. In addition, through interactions with neurotransmitters such as dopamine or serotonin, they can influence other cellular signalling pathways and ultimately lead to behavioural changes such as
Administration of CBD oil to relieve anxiety or combined THC/CBD treatment for seizures (26).
Mechanism of action on brain receptors:
1. Cannabis contains compounds called cannabinoids, which act on the endocannabinoid system (ECS) of the human body.
2. The ECS is involved in the regulation of various bodily functions, including mood, appetite and pain perception.
3. THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), the main cannabinoid in cannabis, binds to CB1 receptors located in the brain and central nervous system.
4. This attachment can lead to cognitive impairment and altered perception.
Short-term effects of cannabis use include changes in perception, mood swings or euphoria, followed by depression or anxiety, impaired coordination, difficulty thinking clearly, slower reaction times, increased heart rate and blood pressure. These effects are usually temporary but, depending on the amount ingested, may last for several hours.

While some studies have shown that some cannabinoids have potential therapeutic benefits for people with conditions such as epilepsy or chronic pain, long-term use has been linked to negative mental health effects, such as an increased risk of psychosis-like disorders such as schizophrenia - but more research is needed in this area before definitive conclusions can be drawn.
Clinical trials with medical cannabis have shown promising results for a variety of conditions such as chronic pain, cancer treatment, epilepsy and more. However, it should be noted that research is still in its early stages and further studies are needed to fully understand the potential benefits of medical cannabis.
While medical cannabis can provide relief for certain conditions, there are also side effects and possible risks associated with its use. Common side effects include dry mouth, dizziness and increased appetite. In addition, long-term use can lead to addiction or cognitive impairment.
It is very important that patients talk to their healthcare provider about medical cannabis as a possible treatment option. Ongoing research on medicinal cannabis will continue to shed light on its potential medical uses and limitations (27).
There are several different ways to consume medicinal cannabis. Vaping offers a quick onset of effect, while edibles have a longer lasting effect. Topical applications can be used for local pain relief without psychoactive effects. It is important to choose the method that best suits your needs and preferences.
Another crucial factor in the effective use of medicinal cannabis is dosage. Start with a low dose and gradually increase it until you achieve the desired effect. Different administration methods such as tinctures, capsules or patches also offer different dosage options. Always seek medical advice before including medical cannabis in your treatment plan to ensure safe and effective use.
Medicinal cannabis can be consumed in a variety of ways, including smoking, vaporisation, edibles and topical applications.
Vaping is increasingly popular for medical cannabis consumption because it poses fewer risks than smoking. Vaping produces vapour instead of smoke, which reduces irritation to the throat and lungs while providing quick relief. Another option is edibles, where THC or CBD (the active ingredients in cannabis) are incorporated into foods such as gummy bears or brownies, which take longer to take effect than smoking or vaping because they must first pass through the digestive system.
Topical applications provide targeted relief from muscle soreness, inflammation and pain without psychoactive effects because they do not enter the bloodstream like other methods. Topical applications come in a variety of forms such as creams, balms or patches so they can be applied throughout the day as needed without interfering with productivity.
In summary, each method of administration offers something unique depending on personal preference and desired duration of effect, so it largely depends on individual needs/preferences as to what works best.
When considering methods of using medical cannabis, it is important to consult a doctor or medical cannabis expert to determine the most appropriate method based on your specific condition and individual needs. Factors such as timing of onset, duration, benefits and drawbacks should be considered to make an informed decision on the method of administration.
Knowing the doses of THC and CBD in medical cannabis is essential to finding the right dose that maximises the benefits without unwanted side effects. Different administration methods for different needs allow users to choose a method that suits their preferences and health condition. It is important to remember that experimentation is necessary to find the right dose for yourself. Doctors titrate the balance between CBD and THC to tailor the medicine to each patient. This ensures that you find the right strength and dosage.
The legalisation of medical cannabis has been a controversial topic in recent years. While some believe it could bring a number of health benefits, others are concerned about possible side effects and addiction problems. However, scientific research into medical cannabis has shown promising results in treating a variety of ailments such as chronic pain, epilepsy, multiple sclerosis and nausea caused by chemotherapy.
As more and more studies demonstrate the efficacy of medical cannabis for certain conditions, lawmakers must consider revising existing laws to allow access to this treatment option where appropriate. The movement to legalise cannabis began in the US and has since been followed by a number of other countries, including Germany and the UK.
Comparison of international guidelines on the use of medicinal cannabis has become a pressing issue due to differences in regulations between countries. While some countries have fully legalised medical cannabis, others are still struggling with its legality and potential health benefits. These policy differences pose a problem for patients who need cannabis-based medicines but have difficulty obtaining them legally.
Another major obstacle for patients seeking treatment with medical cannabis is dealing with conflicting international regulations. Because laws regarding marijuana use vary widely from country to country, users face legal consequences if they cross borders or deal with law enforcement officials who disagree on the matter.

Despite these problems, there is hope for the future prospects of global legalisation of medical cannabis. As more research becomes available demonstrating the potential medicinal benefits of cannabis and as more governments begin to recognise the economic benefits of cannabis, a more unified international policy towards this controversial plant could develop.
In the UK, medical cannabis can only be prescribed for specific conditions when other treatments have proven ineffective. Commonly eligible conditions include severe epilepsy, multiple sclerosis (MS), chronic pain not managed by other therapies, and chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting. The use of medical cannabis is strictly regulated, and it is generally considered a last-resort option under the guidance of a specialist doctor. Medical professionals assess the appropriateness of medical cannabis based on the patient's unique medical needs and response to other treatments.
The first step to accessing medical cannabis in the UK is to consult a specialist doctor, such as a neurologist, pain specialist, or oncologist. During your appointment, provide a detailed medical history, including previous treatments and medications you have tried. The doctor will evaluate your symptoms and determine whether medical cannabis is an appropriate option for your condition. If deemed suitable, the specialist will issue a prescription and refer you to a licensed pharmacy that dispenses medical cannabis.
Once you have your prescription, take it to a licensed pharmacy that is authorized to dispense medical cannabis. Ensure you bring all relevant medical documents, including your diagnosis, treatment history, and any supporting letters from your specialist. These documents are important to validate your prescription and facilitate the dispensing process.
In the UK, medical cannabis is not generally covered by the NHS or private health insurance, and patients usually bear the costs themselves. If you are seeking reimbursement, you may need to submit a claim with your private health insurer, if applicable, along with your prescription and supporting medical documentation. Approval for reimbursement is rare and assessed on a case-by-case basis, so it's important to consult with your insurer to understand their policies regarding medical cannabis coverage.
